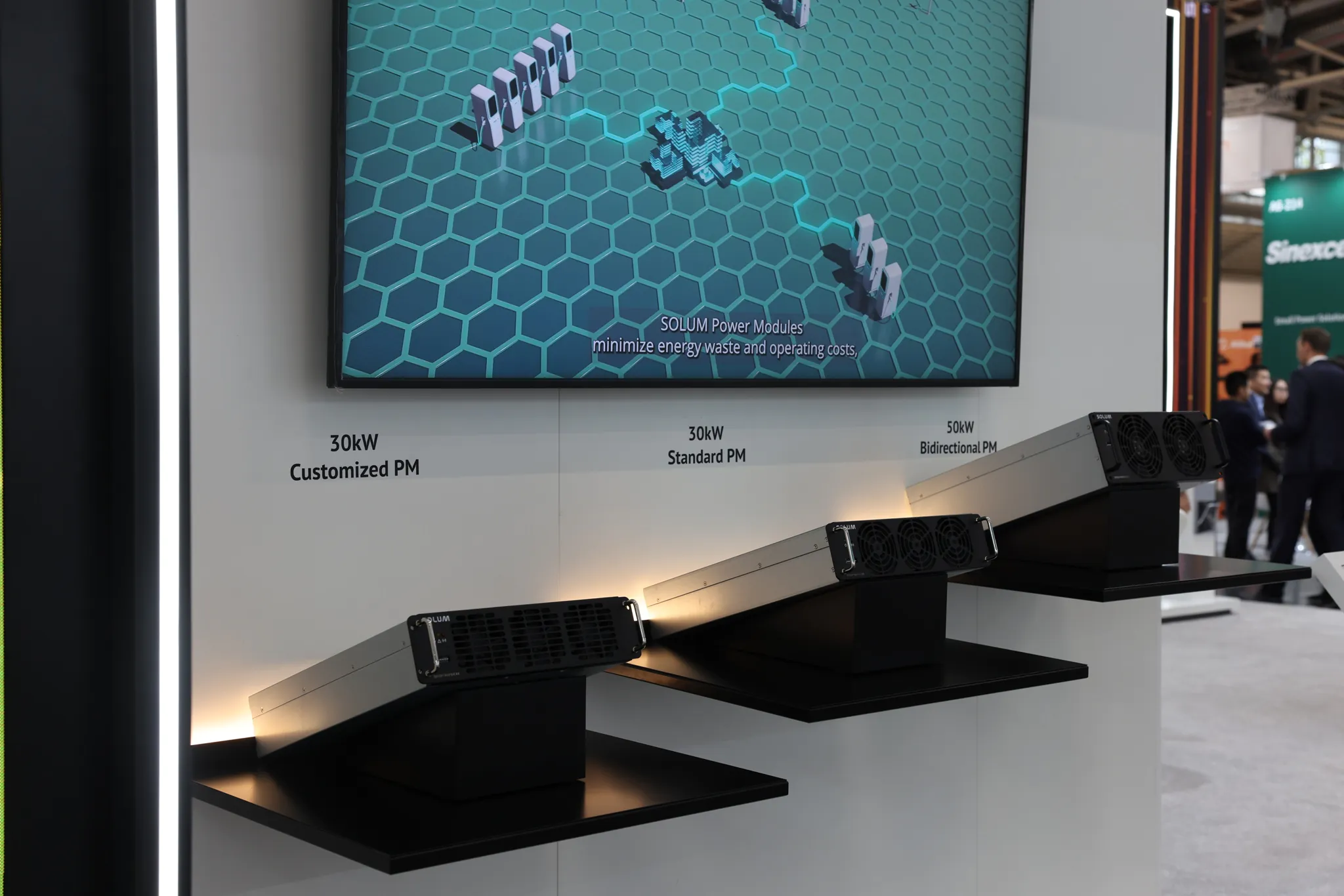
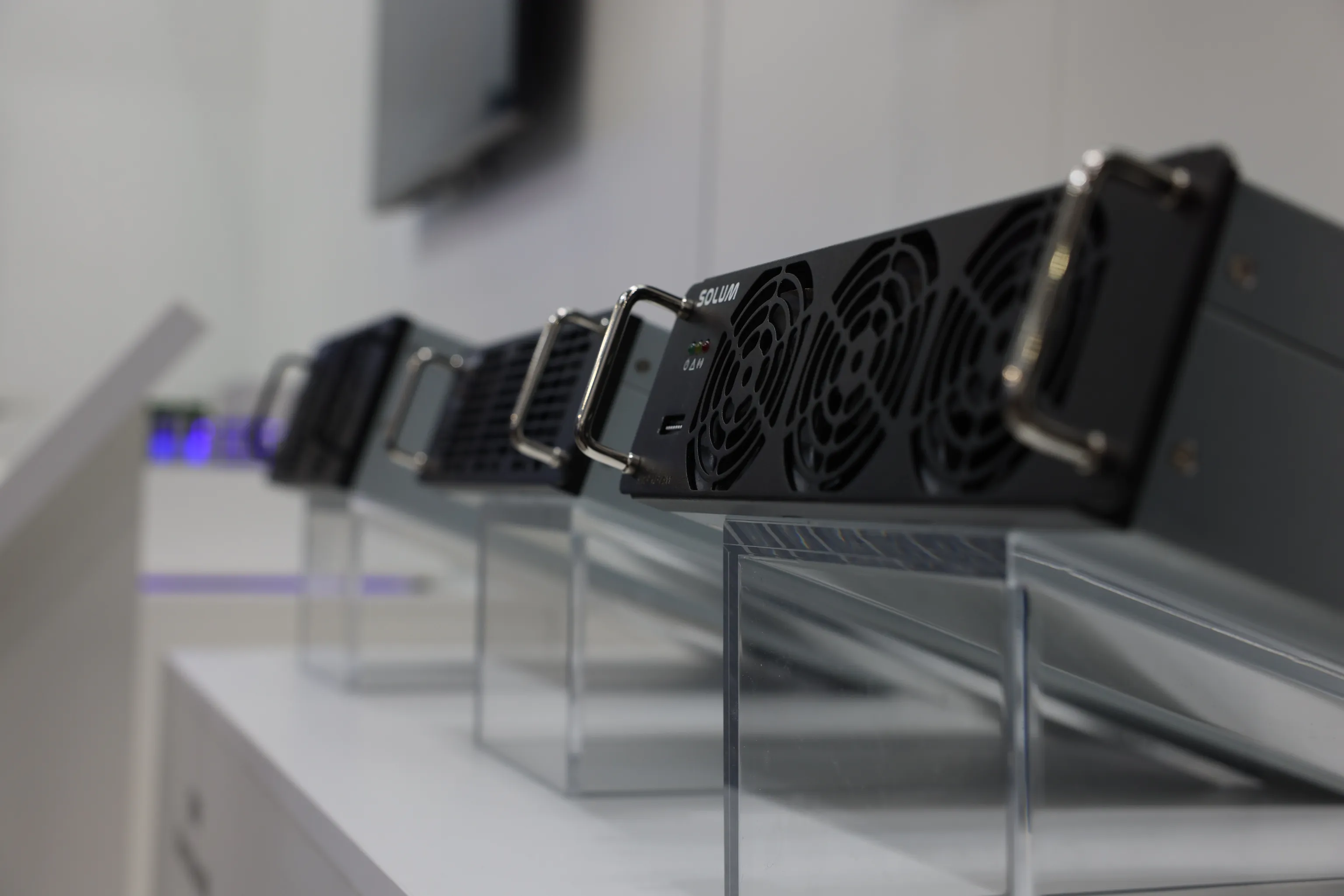
What is a Power Module?
When it comes to electric vehicles or EVs, power is essential. Since EVs are a sustainable solution, they rely on electrical power instead of gasoline or diesel. Without power, electric vehicles won't function. And without properly regulated electrical power, EVs will quickly suffer and deteriorate over time. This is where a power module comes in.
What is a power module?
A power module, also known as a power electric module, is a device containing several power electrical components that work as a single functional unit. Power modules can be used for both commercial and consumer purposes and are commonly found in radios, TVs, computers, phones, and other electronic devices to provide power. It also happens to be a crucial component when it comes to electric vehicles.
For electric vehicles, a power module is a part of their powertrain system that helps manage and regulate the flow of electrical power between the vehicle's battery pack and its electric motor(s). It can also be found in inverters or EV chargers for renewable energies. It plays a significant role in controlling the propulsion system's performance, efficiency, and overall operation. This is how critical power modules are for EVs.
The power module typically contains various components that facilitate the conversion and control of electrical energy. Some of the key components and functions of a power module for electric vehicles include:
- Inverter: The inverter is a central component within the power module that converts the direct current (DC) from the vehicle's battery pack into alternating current (AC) required by the electric motor. This conversion allows for precise control of the motor's speed and torque.
- DC-DC Converter: In addition to the inverter, some power modules also include a DC-DC converter. This component converts the high-voltage DC output from the main battery into the lower-voltage DC needed to power auxiliary systems within the vehicle, such as lights, air conditioning, and infotainment.
- Cooling System: Electric vehicle power modules generate heat during operation, especially during high power demands. A cooling system is incorporated into the module to dissipate this heat and ensure that the components remain within their operating temperature range. Effective thermal management is critical for the longevity and efficiency of the power module and the vehicle itself.
- Control Electronics: The power module includes control electronics that manage the inverter's operation, including adjusting the output frequency and voltage to regulate the electric motor's performance. These electronics may also include safety features and fault detection mechanisms to protect the power module and the overall electric vehicle.
- High-Voltage Connections: Since the power module deals with high-voltage electricity, it is equipped with appropriate connectors and insulation to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards.
Power Electronics: The power module incorporates various power semiconductor devices such as insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) or silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs as well. These components handle the switching of currents and voltages, enabling efficient power conversion and control.
What does a power module do?
Power modules essentially handle the electrical power in an electronic device. It is a great choice for applications where efficiency and space savings are important considerations. A power module offers efficient power conversion from one form to another and provides reliable high-power output for powering different devices and systems. Its main purpose is to provide reliable, safe, and high-performance power to electronic components and systems.
When it comes to an electric vehicle, a power module serves several essential functions that are crucial for the vehicle's operation, performance, and overall efficiency. Here are the main roles of a power module in an EV and a quick rundown of what a power module does:
- Power Conversion: The power module converts the high-voltage direct current (DC) stored in the vehicle's battery pack into the alternating current (AC) needed by the electric motor. This conversion is necessary because most electric motors operate on AC power. The power module's inverter handles this conversion, allowing for the precise control of the motor's speed, torque, and direction.
- Motor Control: The power module's inverter plays a critical role in controlling the electric motor's performance. By adjusting the frequency and voltage of the AC output, the inverter can regulate the motor's speed and torque. This level of control is essential for achieving efficient acceleration, deceleration, and overall driving dynamics.
- Regenerative Braking: The power module enables regenerative braking, a feature in which the electric motor functions as a generator during braking or coasting. The generated electrical energy is then sent back to the battery for recharging. The power module manages this bidirectional energy flow, maximizing energy recovery and extending the vehicle's range.
- Efficiency Optimization: The power module helps optimize the efficiency of the entire powertrain system. By controlling the electric motor's performance and adjusting power delivery based on driving conditions and driver inputs, the power module ensures that the energy from the battery is used effectively, contributing to a longer range and improved energy utilization.
- Thermal Management: Electric vehicle power modules generate heat during operation, particularly under high loads. Effective thermal management is crucial to prevent overheating and maintain optimal operating conditions for the power electronics. The power module often includes cooling systems or heat sinks to dissipate excess heat and ensure component reliability.
- Voltage Regulation: In addition to converting DC to AC, the power module may include a DC-DC converter to regulate the voltage levels within the vehicle. This is important for supplying power to auxiliary systems like lighting, HVAC, and infotainment, which typically require lower voltage levels than the main battery.
- Safety and Protection: The power module incorporates safety features and protection mechanisms to prevent system malfunctions, overloads, and other potential issues. These protections safeguard the power module itself, the electric motor, the battery pack, and the vehicle occupants.
- Integration with Vehicle Systems: The power module is integrated into the vehicle's electronic control system, allowing it to communicate with other onboard systems. This integration enables coordinated and optimized control of various vehicle functions, leading to a smoother and more efficient driving experience.
SOLUM Marketing
Category
Keywords