Every day, the world is becoming more connected through technology, particularly IoT. IoT, which stands for Internet of Things, usually refers to an interconnected network of devices that exchange data and information. This means IoT devices can communicate with each other, or through a cloud, to enhance everyday life and even work.
While IoT is usually found in electronics, machines, and modern appliances, the logistics industry has also started utilizing IoT in recent years. IoT in logistics might be one of the newer developments, but it is making a significant impact in various other industries. Those in the logistics industry can find a multitude of benefits from using IoT in the workplace.
The logistics industry at a glance
The logistics industry encompasses the planning, implementation, and control of the movement and storage of goods, services, and information within a supply chain. It involves a complex network of processes and activities aimed at efficiently managing the flow of resources from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This makes the logistics industry a crucial part of other fields and operations, such as retail, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, food and beverage processing, dining and restaurants, fashion, automotive, and more.
Here’s a glance at the key components and processes within the logistics industry:
- Transportation: This involves the movement of goods and raw materials from one location to another. Modes of transportation include road (trucking), rail, air, maritime, and even pipelines. Trucking delivery is by far the most common and well-known.
- Warehousing and Distribution: Warehousing facilities serve as storage points for goods and materials awaiting transportation or distribution. Distribution centers play a crucial role in sorting, consolidating, and redistributing items to their final destinations, whether they be end consumers or other businesses.
- Inventory Management: Effective inventory management ensures that the right quantity of goods, ingredients, or materials is available at the right time and in the right place. This allows businesses to meet customer demand while minimizing the costs associated with holding excess inventory, reducing profit loss, and minimizing labor costs.
- Supply Chain Management: This involves the coordination and integration of various activities within the supply chain, including procurement, production, inventory management, and logistics, to ensure smooth operations and optimal performance.
- Information Technology: The use of technology, such as transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, is essential. These can be used for tracking shipments, managing inventory, optimizing routes, and enhancing overall visibility and control over the supply chain.
- Freight Forwarding: Freight forwarders act as intermediaries between shippers and carriers, arranging the transportation of goods and handling documentation, customs clearance, and other logistical tasks on behalf of their clients.
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL) and Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL): These are companies that provide outsourced logistics services, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution, to businesses looking to streamline their supply chain operations.
- Last-Mile Delivery: This is the final stage of the logistics process, involving the delivery of goods from distribution centers or warehouses to the end customers' doorstep. Last-mile delivery is often considered the most challenging and costly part of the supply chain due to factors such as traffic congestion and the need for timely and accurate deliveries for end consumers.
Overall, the logistics industry plays a critical role when it comes to facilitating global trade, as well as international and local commerce. According to Statista, the logistics industry was worth over 8.4 trillion euros in 2021. As one of the foundations of international trade, the industry will only continuously evolve and adapt to changing market dynamics, customer demands, and technological advancements, including IoT.
Problems with truck tracking in the past
Truck deliveries and transportation are a big part of the logistics industry, of course. However, truck tracking in the past has not been entirely reliable, and the lack of advanced technology, it has resulted in several challenges and points of conflict.
Here are some of the previous problems with truck tracking.
- Limited Visibility: Traditional tracking operations often relied on manual processes or basic technologies that provided limited visibility into the location and status of shipments. This lack of real-time information made it difficult for logistics companies to accurately track and manage their fleets.
- Inaccurate Data: Manual data entry and paper-based systems were prone to errors and inconsistencies. This has led to inaccurate tracking information in the post, and delays in identifying issues or discrepancies in the supply chain.
- Communication Barriers: Poor communication between different stakeholders in the supply chain, such as shippers, carriers, and consignees, hindered effective tracking and coordination of shipments.
- Miscommunication often leads to delays, missed deliveries, dissatisfied customers, and increased costs.
- Limited Integration: Legacy tracking systems in the past often lacked integration with other logistics and transportation management systems. This made it difficult to share data and coordinate activities across different functions or departments within a business or organization.
- Cost and Scalability: Implementing and maintaining tracking systems, especially those based on proprietary hardware or software, could be costly and difficult to scale as the business grows or as technology evolves.
- Security Concerns: Traditional tracking methods were susceptible to security threats due to limited monitoring, a lack of technology, and control over shipments during transit. This includes threats such as theft or tampering of records or goods.
- Environmental Factors: Challenges such as adverse weather conditions, traffic congestion, and infrastructure limitations could affect the accuracy and reliability of tracking systems. Without the right technology in the past, these environmental problems led to delays and disruptions in the supply chain.
These examples of truck tracking challenges in the past highlight the need for more advanced tracking solutions as well as modern integration of systems. Logistics professionals who leverage new technologies, such as GPS (global positioning system), RFID (radio frequency identification), IoT, and more, can elevate their businesses into the modern world. With technology, they can avoid these truck tracking challenges—they can have real-time visibility, improve efficiency, have better communication, and foster better collaboration across the entire logistics ecosystem.
How IoT helped improve truck and delivery tracking
The Internet of Things (IoT) has played a significant role in revolutionizing truck and delivery tracking over the past few years. Now, with advanced technology, the logistics industry can move further into modernization and keep up with the demands of the modern world.
Here are the particular uses of IoT in logistics and how it has improved truck and delivery tracking:
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
IoT devices, such as GPS trackers and sensors, can be installed on trucks, containers, and actual packages. This allows employees to continuously monitor their location, temperature, humidity, and other relevant parameters in real time. This real-time visibility allows logistics companies to accurately track shipments and proactively address any issues or delays that may arise during transit.
Route Optimization
IoT-enabled tracking systems can analyze data on traffic conditions, weather forecasts, and historical route performance to optimize delivery routes in real time. By identifying the most efficient routes and anticipating environmental factors, logistics companies have more chances to streamline their routes. They can reduce fuel consumption, minimize transportation costs, and improve on-time delivery performance.
Condition or Quality Monitoring
There are IoT sensors that can monitor the condition and integrity of goods during transit. This includes temperature-sensitive or perishable items, like fresh produce, food and beverage items, medicines, and drugs. If the sensors detect any deviations from predefined thresholds, alerts can be sent to logistics managers. This enables managers and couriers to take immediate corrective actions to prevent spoilage or damage to the goods.
Fleet Management and Maintenance
IoT also helps in fleet management and maintenance for any logistics warehouse or facility. IoT-enabled devices can monitor the precise location of trucks and delivery vehicles in real-time, as well as their health and performance. This enables logistics companies to detect potential maintenance issues before they lead to costly breakdowns or disruptions. By implementing predictive maintenance strategies, companies can minimize downtime, extend the lifespan of their assets, and improve overall fleet reliability.
Inventory Management
IoT sensors can be deployed in warehouses and storage facilities to monitor inventory levels continuously. These sensors track the movement of goods, provide real-time updates on stock levels, and automatically trigger reorder notifications when needed. Managers will also be able to access precise tracking of inventory location within a facility to streamline audits and search times, as well as minimize the risk of loss and theft. They can also aid in shelf-life monitoring, especially for perishable goods, ensuring that products are stored within optimal conditions.
Digital BOL Implementation
BOL, or bill of lading, is a crucial document that represents the receipt of cargo, and with IoT, it can be digitized. IoT devices, such as specific tablets or mobile devices, can be used to digitize the BOL process. Drivers can capture electronic signatures, scan barcodes, and upload documents directly into digital systems. This eliminates the need for paper-based documentation that can be tampered with or contain errors. It also reduces administrative overhead.
Smart Warehousing
IoT in logistics can also be beneficial in creating or maintaining a smart warehouse. IoT sensors can automate inventory tracking and replenishment processes. Smart shelves and bins can be equipped with sensors that detect item movement and inventory levels in real time, which can trigger automated reorder notifications and stock replenishment.
IoT devices can also monitor environmental conditions, including temperature, humidity, and air quality, within the warehouse. This data can be used to optimize storage layouts, improve ventilation, and ensure optimal conditions for sensitive or perishable goods.
Enhanced Security
IoT devices can provide enhanced security features as well. This includes tamper detection and geofencing, which can protect shipments from theft, unauthorized access, or tampering. By monitoring the movement and location of goods in real time, logistics companies can quickly identify and respond to security incidents, reducing the risk of loss or damage to the cargo.
Data Analytics
IoT-generated data can be analyzed using advanced analytics techniques to derive actionable insights and optimize various aspects of logistics operations, such as inventory management, demand forecasting, and customer service. By leveraging IoT data analytics, logistics companies can make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Overall, IoT in logistics has transformed truck and delivery tracking for the better. Now, managers have unprecedented visibility, drivers have more control and security, and the whole business has intelligence and collaboration across the entire supply chain. IoT in logistics enables companies to operate more efficiently and competitively in the current business environment.
How does IoT in logistics work?
IoT in logistics works by leveraging interconnected devices, sensors, and data analytics to gather real-time information about assets, shipments, and processes within the supply chain. Together, these interconnected devices automate and streamline operations that were once done manually.
Here's how IoT is typically being implemented in logistics now:
- Deployment of IoT Devices
Logistics companies deploy IoT devices, such as trackers, tags, temperature sensors, humidity sensors, and accelerometers, on various assets, including trucks, containers, packages, and inventory items. These devices are equipped with connectivity capabilities to transmit data to centralized systems or cloud platforms. - Data Collection
IoT devices collect a wide range of data about the location, condition, and status of assets and shipments throughout their journey in the supply chain. For example, IoT trackers provide real-time location information, temperature sensors monitor the environmental conditions of perishable goods, and RFID tags track the movement of inventory items within warehouses or distribution centers. - Data Transmission
The data collected by IoT devices is transmitted to centralized systems or cloud platforms via wireless communication networks. Depending on the application, data transmission may occur in real-time or periodically at established periods. - Data Processing and Analysis
Once the data is transmitted to centralized systems or cloud platforms, it is processed and analyzed using advanced analytics techniques. This includes identifying patterns, trends, anomalies, and insights from the data to improve decision-making and optimize various aspects of logistics operations. - Actionable Insights and Automation
The insights derived from IoT data analysis enable logistics companies to take proactive actions to optimize their operations. This includes predictive maintenance algorithms and route optimization algorithms that can reduce maintenance costs, fuel refilling, errors, and more. - Integration with Existing Systems:
IoT in logistics is often integrated with existing systems. This includes transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This integration enables seamless data exchange and coordination across different functions or departments within an organization.
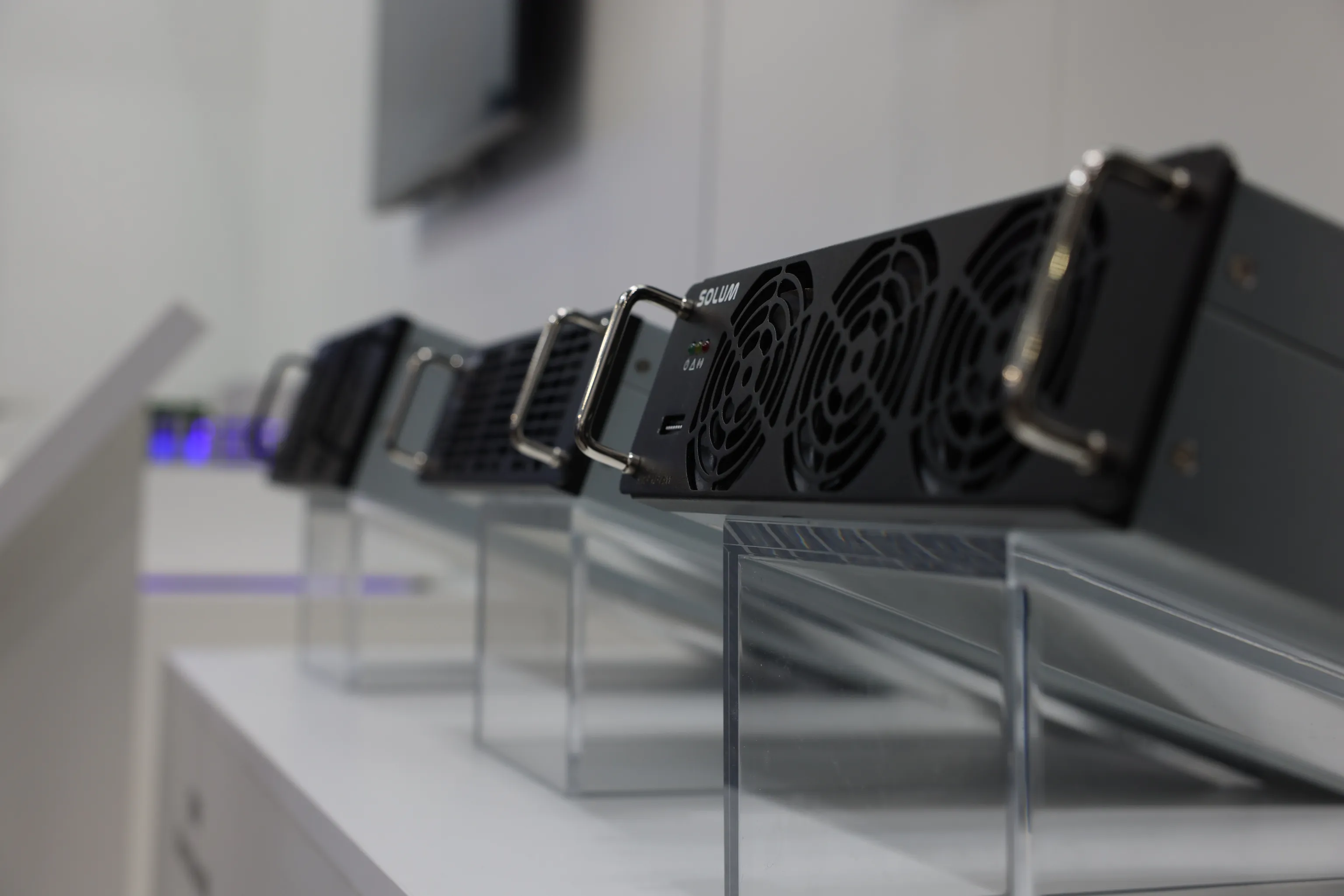
SOLUM Industrial Tracker for truck tracking
The SOLUM Industrial Tracker is a great example of IoT in logistics. This worker and asset tracking solution from SOLUM Group is innovative and efficient, helping industrial companies manage and protect their inventory and employees.
The SOLUM Industrial Tracker is a specialized GPS tracker made for various applications in the industrial environment. It can be used for oil rig operations, warehouse and manufacturing plants, construction sites, and more.
For truck tracking, it can be used by logistics companies to manage their fleet and goods. The SOLUM Industrial Tracker is equipped with:
- A built-in GPS tracker (for real-time tracking and visibility)
- A multi-GNSS motion sensor (for increased location accuracy)
- LoRa connectivity (for fast data transfer, large bandwidth, and long-distance communication)
- Deployable cloud software (for geofencing capabilities, automatic safety incident alerts, and time and attendance data collection)
- IP67 certification (for harsh conditions)
With wider coverage, durability, reliability, and better accuracy, the SOLUM Industrial Tracker makes for an ideal truck-tracking solution for all kinds of logistics companies.
Do you think you need a tracking solution like this for your fleet? Contact SOLUM experts now and know how the SOLUM Industrial Tracker can revolutionize logistics operations in your business!