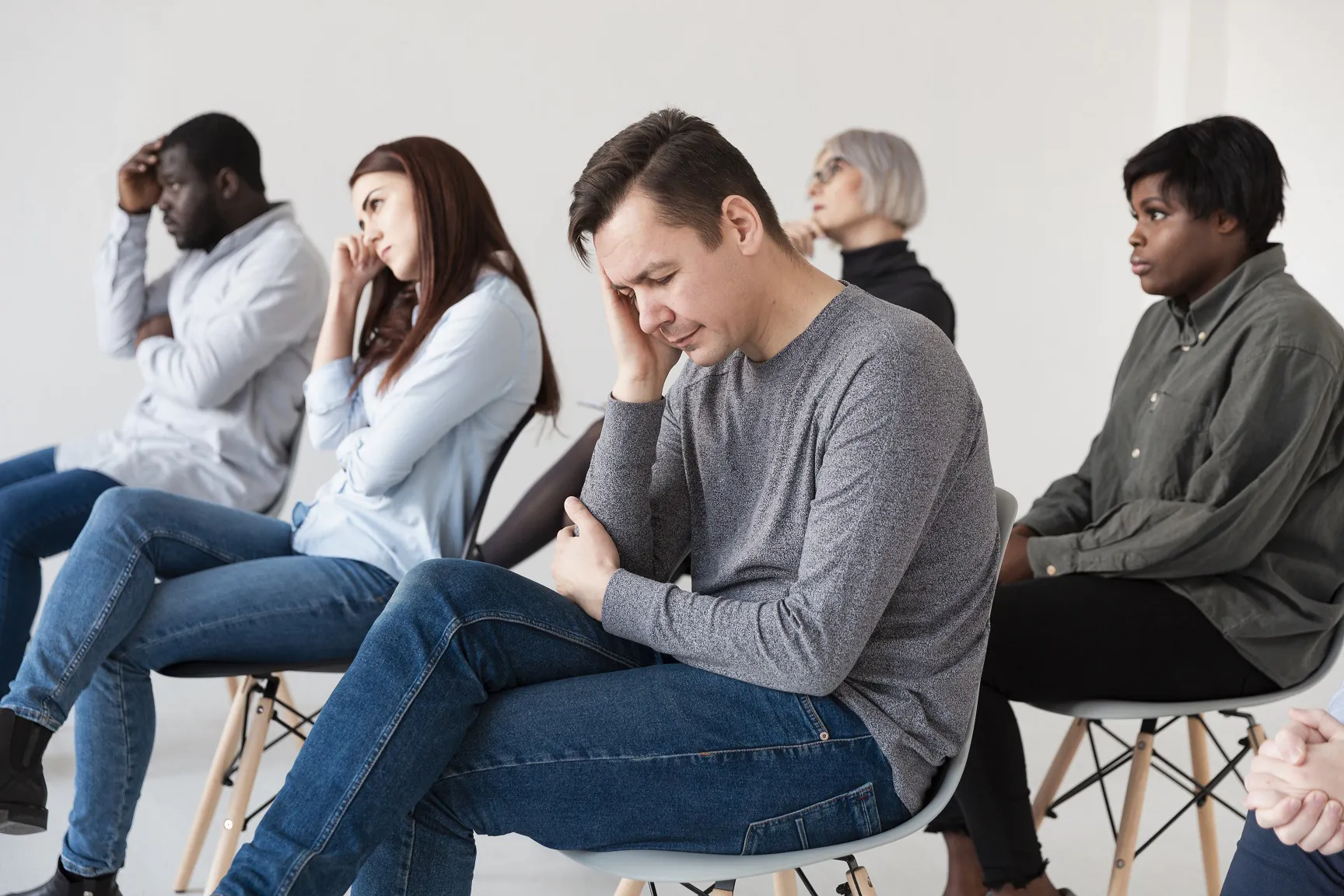
Mental health awareness and services still have a long way to go. In the modern world, the mental health crisis is becoming more widely talked about. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), anxiety and sadness increased by 25% worldwide in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Because of this, mental health care is becoming more and more accepted. The problem is that mental health centers need to keep up with the demand for mental health care. With a workforce shortage and gaps in accessibility, mental health centers and patients would need to rely on other solutions to improve mental health treatment.
Common mental issues treated by mental health centers
Mental health centers treat a wide range of mental issues or disorders nowadays. All of them offer various kinds of treatment and therapies and generally offer a safe space for people seeking help for their mental health.
Here are some of the common mental issues being treated at mental health centers:
- Depression: Depression is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. It can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. Treatment by mental health centers often involves a combination of therapy, medication, and recommended lifestyle changes.
- Anxiety disorders: Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and various phobias. Symptoms may include excessive worrying, panic attacks, avoidance behaviors, and physical symptoms like palpitations or sweating. Behavioral health centers may offer treatments typically involving therapy, medication, and relaxation techniques to manage symptoms and improve coping strategies.
- Bipolar disorder: Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood swings that include periods of mania (elevated mood, impulsivity) and depression. These mood fluctuations can disrupt daily life, work life, and relationships. Treatment often includes mood stabilizers, therapy to develop coping skills, and lifestyle adjustments depending on the situation and the severity of the disorder.
- Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by disturbances in thinking, perceptions, emotions, and behavior. Symptoms may include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and impaired social functioning. People usually come to mental health centers and receive a combination of antipsychotic medication, therapy, and support services to manage schizophrenia symptoms and improve functioning in their daily lives.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): OCD involves recurring, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety or preventing a feared outcome. These behaviors can be long-lasting, and can significantly interfere with daily life. Behavioral health centers may offer cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, and exposure and response prevention techniques. These will help reduce symptoms, improve functioning, and help manage persisting behaviors.
- Substance Abuse or Use Disorders: Problematic use or consumption of alcohol, drugs, or other substances can also lead to significant harm or distress. These can also lead to long-lasting health dangers if not treated properly. Mental health centers can offer medication, counseling, cognitive and behavioral therapies, detoxification, and more. These can help people with substance use or abuse disorders reduce symptoms, manage side effects, avoid relapse, and achieve a successful recovery.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): PTSD can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This mental health disorder is often characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, hypervigilance, and the avoidance of reminders of the trauma. It can significantly impair relationships and daily functioning, especially for those with extreme or complex PTSD. Treatment often includes therapy, medication, and techniques to process and cope with the traumatic experience.
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that starts in childhood and continues into adulthood. It is usually characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. ADHD can affect both children and adults, impacting academic, occupational, and social functioning. Treatment typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications. These will help manage symptoms and improve daily functioning for those affected by this disorder.
- Eating disorders: Eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder involve unhealthy attitudes and behaviors surrounding food, weight, and body image. These disorders can have serious physical and psychological consequences for people if left untreated. Mental health centers may offer multidisciplinary approaches involving medical care, nutritional counseling, therapy, and support groups to address underlying issues and promote recovery.
- Other personality or behavioral disorders: other disorders such as borderline personality disorder, narcissistic personality disorder, and antisocial personality disorder can also affect people and how they interact with people and their surroundings. These involve enduring patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience that deviate from cultural norms. Behavioral health centers will usually offer therapy, medication, and various counseling services to treat these illnesses.
These are just a few examples of mental health disorders that would need treatment from mental health centers and mental health professionals. There are many other mental health issues and disorders that mental health centers may address through various forms of therapy, medication management, technology and devices, and other interventions.
Top challenges when it comes to mental health care
Providing mental health care in a modern world has some unique challenges. Although perceptions towards mental health and mental health care have improved and technological advancements have led to discoveries enhancing mental health diagnosis and care, there are still certain difficulties that both patients and health care providers may face.
These challenges may impact the delivery, accessibility, and effectiveness of mental health care and services.
- Stigma: Stigma remains one of the most significant barriers to seeking and receiving mental health care. Stigma can lead to discrimination, social isolation, and reluctance to seek help due to fear of judgment or negative attitudes towards mental illness. This can prevent affected individuals from accessing necessary treatment and support.
- Access to Care: Disparities in access to mental health care exist due to various factors as well. This includes geographic location, socioeconomic status, insurance coverage, and other cultural barriers. Many people, particularly those in rural or underserved areas, may face challenges accessing mental health services due to transportation issues, financial constraints, or even a lack of providers or technology.
- Provider Shortages or Human Resource Shortage: There is a shortage of mental health professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, and counselors, particularly in certain regions and specialty areas. In the United States, 160 million Americans live in areas with mental health professional shortages in 2023. In fact, over 8,000 more professionals are needed to ensure an adequate supply and mental health treatment. This kind of shortage contributes to long wait times for appointments, limited availability of services and care, and increased workload for existing providers.
- Cost of Care: Mental health care can be expensive. Because of this, many individuals may struggle to afford treatment or medication, especially if they lack adequate insurance coverage or have high out-of-pocket expenses. The cost of therapy sessions, psychiatric medications, and other mental health services can create financial barriers to accessing the right care.
- Integration with Physical Health Care: The integration of mental health care with primary care and other medical services is essential for addressing the holistic needs of individuals. However, systemic barriers, such as fragmented healthcare systems, limited communication between providers, and reimbursement challenges, can hinder collaboration and coordination of the best care possible.
- Cultural Competence and Diversity: Cultural factors influence individuals' perceptions of mental health and help-seeking behaviors as well. Providing culturally competent care requires understanding and respecting the diverse backgrounds, beliefs, and values of clients. However, there may be a lack of cultural competence among mental health providers, leading to disparities in treatment outcomes for minority populations.
- Treatment Resistance and Non-Adherence: Some individuals with mental health disorders may be resistant to treatment or struggle with medication adherence, therapy attendance, or engagement in recommended interventions. Factors contributing to treatment resistance and non-adherence include stigma, side effects of medications, a lack of insight into the illness, as well as social or environmental stressors.
- Prevention and Early Intervention: While there is increasing recognition of the importance of prevention and early intervention in mental health care, resources and funding for these initiatives may be limited. Additionally, identifying and reaching individuals at risk of developing mental health disorders before symptoms escalate can be challenging due to barriers or other factors. This might include stigma, a lack of awareness, and limited access to screening and preventive services.
These challenges may require a multifaceted approach involving advocacy, policy changes, public education, the expansion of the workforce, and specific technological advancements.
How brainwave sensors can manage mental issues
One technological advancement that can help provide mental health care for individuals is brainwave sensors. Brainwave sensors, usually utilizing electroencephalography (EEG) sensors, measure the electrical activity of an individual’s brain. These sensors can play a role in providing health care and bridging gaps between healthcare professionals and patients. When used correctly, they can help manage mental health issues and disorders in several ways.
- Biofeedback Therapy
- Neurofeedback Therapy
- Assessment and Diagnosis
- Treatment Facilitation and Monitoring
- Research and Understanding
- Wearable Devices for Self-Tracking
Biofeedback Therapy
EEG-based biofeedback therapy uses real-time feedback from brainwave activity to teach individuals how to self-regulate the function of their brains. By monitoring their brainwaves, individuals can learn to control physiological responses such as stress, anxiety, or attention levels. This can be particularly helpful for people with mental health conditions like anxiety disorders, ADHD, and PTSD.
Neurofeedback Training
Neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback therapy that specifically focuses on training individuals to modify their brainwave patterns. By providing feedback on brainwave activity, individuals can learn to enhance desirable patterns associated with relaxation, focus, or mood stability, while reducing patterns associated with symptoms of mental health disorders.
Assessment and Diagnosis
EEG devices can assist in the assessment and diagnosis of certain mental health conditions. Patterns of brainwave activity may indicate specific disorders such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, or attention deficits. Apart from this, brainwave sensors might also contribute to detecting brain injuries and related brain disorders. EEG-based assessments can provide objective data to complement clinical evaluations and inform treatment decisions for various mental conditions.
Treatment Facilitation and Monitoring
Apart from condition assessment and diagnosis, brainwave sensors can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment interventions over time. Sensor-based rehabilitation for neurological diseases can be expected, offering insights into the effects of treatments on one’s brain. By tracking changes in brainwave patterns, mental health centers and professionals can assess the progress of individuals undergoing therapy, medication management, or other interventions for mental health disorders and neurological diseases. This kind of feedback can help optimize treatment strategies for different patients and situations, and adjust approaches as needed.
Research and Understanding
Brainwave sensors contribute to research efforts as well. They can be used to better understand the neurobiology of mental health disorders. By studying brainwave patterns in individuals with different conditions, researchers can identify biomarkers and clarify underlying mechanisms. They also have the chance to develop more targeted interventions for prevention and treatment of various conditions.
Wearable Devices for Self-Tracking
Advances in technology have led to the development of wearable devices with EEG sensor capabilities as well. Individuals can use these for self-tracking and monitoring their mental well-being. These devices can provide insights into patterns of brain activity associated with stress, relaxation, sleep quality, and cognitive performance. As a result, this empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their mental health.
While brainwave sensors hold promise for managing mental health issues, it's important to also remember that they may have limitations and that the opinions of their qualified healthcare provider or professionals are also crucial. For complex or intense mental health issues, people will need to ensure that certain devices are part of comprehensive treatment plans or are recommended by mental health centers.
MINDY features that can help mental patients and individuals
The MINDY Brainwave Sensor developed by SOLUM Group is a good example of a brainwave sensor as a mental healthcare device. MINDY is a wearable multisensor headband device that can provide real-time feedback regarding brain activity, heart rate, breathing, and body movements. Apart from that, this brainwave sensor has various features that can aid in a journey of health and mindfulness.
- Guided meditation
- Relaxation exercises
- Mindful workouts
Guided meditation for individuals with anxiety issues
MINDY, together with its Mindy App, can provide guided meditations to users. This can be beneficial for individuals with anxiety issues and other mental conditions. This is because MINDY makes it easy for people to incorporate meditation into their daily routines. They can use this SOLUM Brainwave Sensor to find peace of mind and achieve calmness through chaos and unease.
Relaxation exercises for individuals with sleeping difficulties
For people with sleeping difficulties, such as insomnia, they can also find help from SOLUM MINDY. This Brainwave Sensor can guide people through relaxation exercises and meditation to help them achieve a better quality of sleep. Sleeping difficulties can result from various factors, such as stress, anxiety, lifestyle changes, other health conditions, and more. MINDY can help users enter a more relaxed state of mind, helping them sleep soundly and more consistently.
Mindful workouts for individuals with behavioral disorders
MINDY can also encourage people to exercise daily. Exercise can help alleviate stress and elevate moods, offering individuals with behavior disorders a better way to manage their emotional and mental state. Those with OCD, ADHD, depression, and more can practice mindful workouts with the SOLUM Brainwave Sensor. Not only does this help strengthen the body, but it also soothes the mind.
Overall, MINDY can be used by individuals to monitor and take care of their mental and physical well-being. With its various sensors and technology, as well as its app, individuals and mental health centers can leverage this Brainwave Sensor when it comes to mental health care and treatment.
Contact SOLUM Group experts now and find out more about SOLUM MINDY!